Wrist Arthroscopy
What is wrist arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is a type of laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery used to diagnose and treat joint problems. It can be used to look inside the joint of the wrist, and various surgeons employ many techniques. Arthroscopy is performed on many parts of the body, and wrist arthroscopy is one of the most common arthroscopic procedures.
Why is wrist arthroscopy performed?
Wrist arthroscopy allows the doctor or surgeon to examine the inside part of the wrist joint, including ligaments and the surface of cartilage, which can help them to determine if there is an internal problem in the wrist. The procedure may be performed after an injury, such as a fall, or when the wrist has twisted. There may be some swelling, clicking, or bruising, which can lead a medical professional to believe further investigation is necessary.
Wrist arthroscopy can also help to align wrist fractures, remove (wash away) infection, remove the excess joint lining from conditions such as inflammatory arthritis, and remove ganglions (a fluid-filled swelling).
What does wrist arthroscopy involve?
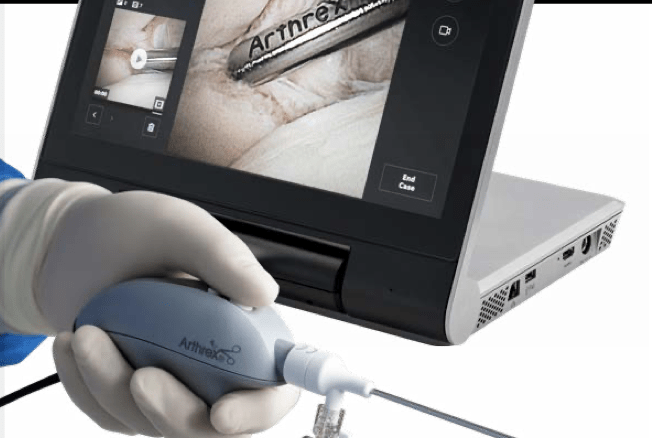
An arthroscope is a small camera that is fixed to the end of a long, narrow tube. This tube is inserted into the body through a small cut made in the back of the wrist joint. The camera allows the surgeon to see inside the wrist joint through direct projection on the screen in front of them. Further cuts can be made to allow the surgeon to see inside different areas of the wrist joint. This also allows the surgeon to repair the ligament if necessary.
How can you prepare for wrist arthroscopy?
Usually, there is no specific preparation the patient needs to do before the procedure. It is advisable to arrange transport or to arrange for someone to help the patient get home after the procedure. The patient must give their medical history and tell the surgeon which kinds of medicine they are taking, and they will be advised accordingly which they are able to continue with. Blood-thinners must be temporarily avoided before surgery (common blood thinners are ibuprofen and aspirin). These details will all be discussed pre-surgery, so the patient is always aware of what is expected of them.
Post-operative care
After the procedure, the wound is closed with stitches, and a bandage is placed around the wrist, which limits motion. This allows for faster recovery, as it will protect the wrist area and support helps to relieve pain. As arthroscopy is usually performed as a day-case procedure, there is not normally an overnight stay in the hospital. The patient can go home the same day and is advised to keep their wrist elevated for a few days after surgery in order to minimise swelling. Cold packs can help with swelling too.
Some patients may need to wear a splint which will provide them with support. If a dressing is applied, it may need to be changed, and correct aftercare advice will be given by the healthcare provider. Physical therapy or specific hand exercises may be advised to help the patient regain the full range of motion.