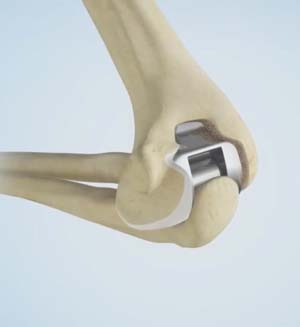
Total/ Hemi Elbow Replacement (Arthroplasty)
What is it?
Total elbow arthroplasty replaces a native elbow joint with a synthetic elbow joint (usually made of metal and plastic).
When is elbow arthroplasty surgery recommended?
There are two major indications for elbow replacement surgery.
⦁ Elbow arthritis
⦁ Rheumatoid arthritis
⦁ Sequelae to elbow trauma
⦁ Unreconstructable acute fracture in the elderly
What does the operation involve?
Prof Imam will be able to explain what will happen to you. In most cases, surgery is performed under a general anaesthetic, which means that you will be asleep for the operation. In many cases, the anaesthetic doctor will also recommend an arm block, an injection around the shoulder to temporarily prevent the nerves in the arm from carrying pain signals to the brain. This block aims to lessen the elbow’s post-operative pain, but it will also have the effect of temporarily paralyzing the arm on the day of the surgery.
Your surgeon will usually cut the back of the elbow to remove the damaged elbow and implant an elbow replacement. After the surgery, you will have a bandage on the elbow, and you may also have a splint to rest the elbow. Most surgeons will aim to move the elbow as soon as possible after the surgery to reduce stiffness. Resting splints may be used for several weeks, especially at night. Physiotherapy is recommended after this type of surgery. You can expect to stay in hospital for between two and five days.
What is the aim of this operation?
Elbow replacement surgery aims to give you a pain-free, mobile elbow that enables you to perform everyday activities. After this surgery, it is recommended that the arm is not used to carry heavy objects or for heavy manual activities as these may lead to early replacement failure.
Hemiarthroplasty
What is Hemiarthroplasty?
Hemiarthroplasty of the elbow replaces one part of a native elbow joint with an artificial elbow joint (usually made of metal). Usually, the surgery involves replacing the end of the humerus (upper arm) bone at the elbow joint.
When is hemiarthroplasty surgery recommended?
The only indication for a hemiarthroplasty is elbow trauma, where the bone is broken so badly that it cannot be fixed in the usual way. This procedure is usually only recommended in more older adults who may have fewer demands of the elbow.
What does the operation involve?
The surgeon will be able to explain what will happen to you. In most cases, surgery is performed under a general anaesthetic, which means you will be asleep for the operation. In many cases, the anaesthetic doctor will also recommend an arm block, an injection around the shoulder to temporarily prevent the nerves in the arm from carrying pain signals to the brain.
Your surgeon will usually cut the back of the elbow to remove the damaged elbow and implant an elbow hemiarthroplasty. After the surgery, you will have a bandage on the elbow, and you may also have a splint to rest the elbow. Most surgeons will aim to move the elbow as soon as possible after the surgery to reduce stiffness. Resting splints may be used for several weeks, especially at night. Physiotherapy is recommended after this type of surgery. You can expect to stay in hospital for between two and five days.
What is the aim of this operation?
Elbow replacement surgery aims to give you a pain-free, mobile elbow that enables you to perform everyday activities. It is recommended that after this surgery, the arm is not used to carry heavy objects or for heavy manual activities as these may lead to early failure of the replacement.
What are the risks of Total Elbow Replacement Surgery?
The risks of this surgery can be divided into the risks of the anaesthetic and the risks of the surgery itself. Your anaesthetic doctor will be able to advise you of the risks of the anaesthetic.
What are the risks of Elbow Replacement Surgery?
The risks of this surgery can be divided into the risks of the anaesthetic and the risks of the surgery itself. Your anaesthetic doctor will be able to advise you of the risks of the anaesthetic.
The common risks of elbow replacement surgery include:
⦁ Infection
The risk of infection is approximately 2 out of 100 cases within one year of surgery. Late infection can occur and increases the overall rate up to 5 in 100 cases. If the elbow replacement becomes infected, it will most likely have to be removed to get the infection under control.
⦁ Dislocation
This means that the two parts of the elbow replacement move out of position so that they do not join correctly. This is often painful. The risk is reduced by linking the two parts of the joint together, but this increases the risk of the elbow replacement becoming loose within the bone. Surgery may be needed to put the elbow back into position without opening the elbow (manipulation under anaesthetic, MUA) or by an operation to open the elbow and join the two parts together. Occasionally revision surgery may be required.
⦁ Fracture of the bones around the elbow
The bones around the elbow may break (fracture) either during the surgery if they are very fragile or after surgery as a result of the elbow replacement loosening in the bone or after a fall. Further surgery may be needed to address this.
⦁ Nerve injury
The nerve that is at the greatest risk of injury is the ulnar nerve. This nerve passes around the back of the elbow joint and supplies the feeling in the little and ring finger and also some of the muscles in the hand. If this nerve is injured, you may experience pins and needles or numbness in the little finger or weakness in the hand. These symptoms usually recover but may be permanent.
⦁ Implant loosening
The elbow replacement is usually fixed into the bone using cement that acts like the grout on wall tiles. With time the replacement may become loose in the bone, leading to pain or fracture of the bone. Your surgeon will usually monitor your elbow replacement after surgery with X-rays to look for signs of this loosening. If the implant becomes loose, your surgeon will usually recommend surgery to revise the elbow replacement.